- Published on
ReentrantLock에 대한 개인적인 정리
- Authors

- Name
- 이건창
Introduction
ReentrantLock 간단하게 알기
객체에 내제된 잠금장치는 외부에서 해제할 수 없지만 ReentrantLock은 특정 외부에서 해제할 수 있다. 해제할 수 있는 방법은 timeout 이거나 interrupt 를 이용한다.
해제하는 상황은 다음과 같다.
- 락 획득 대기 시간을 설정으로 인해
- 인터럽트를 이용해
락 획득 대기 시간을 설정으로 인한 경우
ReentrantLock의 tryLock(...) 메서드를 이용하면 락 획득 대기 시간 설정이 가능하다.
class Philosopher(
private val left: ReentrantLock,
private val right: ReentrantLock,
private val random: Random = Random(),
) : Thread() {
override fun run() {
try {
while (true) {
sleep(random.nextInt(1000).toLong())
left.lock()
try {
if (right.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
try { sleep(1000) } finally { right.unlock() }
} else {
println("${currentThread().name} gave up on right fork")
}
} finally { right.unlock() }
}
} finally { left.unlock() }
}
}
tryLock명령어는 지속되는 데드락을 피할 수 있지만 일부 요청이 실패하게 된다. 또한 라이브락이라는 현상에 자유롭지 않다.라이브락은 모든 스레드가 동시에 타임아웃을 발생시키고 곧바로 데드락 상태에 빠지는 것을 의미한다. 해당 문제는 서로 다른 타임아웃 값을 설정해 가능성을 줄일 수 있겠지만
tryLock명령어 자체가 좋은 해결방법은 아니다.
인터럽트를 이용한 경우
ReentrantLock의 lockInterruptibly 명령어를 사용하면 인터럽트를 발생시켜 동작을 무효화할 수 있다.
fun main() {
val l1 = ReentrantLock()
val l2 = ReentrantLock()
val thread1 = Thread {
try {
l1.lockInterruptibly()
l2.lockInterruptibly()
Thread.sleep(1000)
} catch (e: InterruptedException) {
println("Thread 1: interrupted")
}
}
val thread2 = Thread {
try {
l2.lockInterruptibly()
l1.lockInterruptibly()
Thread.sleep(1000)
} catch (e: InterruptedException) {
println("Thread 2: interrupted")
}
}
thread1.start()
thread2.start()
thread1.interrupt()
thread2.interrupt()
thread1.join()
thread2.join()
}
ReentrantLock 자세히 알기
ReentrantLock 작성된 문서는 다음과 같다.
내용을 정리해봤다.
ReentrantLock은 공정성 옵션을 추가할 수 있다. 공정성 옵션을 추가하면 오래 대기한 스레드부터 실행한다.- 많은 스레드에서 공정한 잠금을 사용하면 사용하지 않은 경우보다 전체 처리량이 낮아질 수 있지만 잠금을 획득하고 기아 상태가 없을을 보장하는 시간적 차이가 더 적다.
- 잠금의 공정성은 스레드 스케줄링의 공정성을 보장하지 않는다. 그래서 여러 스레드 중 특정 스레드가 잠금을 하는 경우가 많을 수 있다.
- 시간이 설정되지 않은
tryLock은 공정성 설정을 따르지 않는다.
Maximum lock count exceeded 이슈
잠금을 보유한 횟수로 얼만큼 획득하려는지 확인할 수 있다. 일정값이 넘어가면 예외가 발생한다.

ReentrantLock은 동일한 스레드에 의한 잠금을 최대 Int 최대값까지만 지원한다. 그 이상은 Error 가 발생한다. tryLock에서 int 자료 구조로 스레드로 상태를 확인하고 오버 플로우가 발생하면 Maximum lock count exceeded이슈가 발생한다.
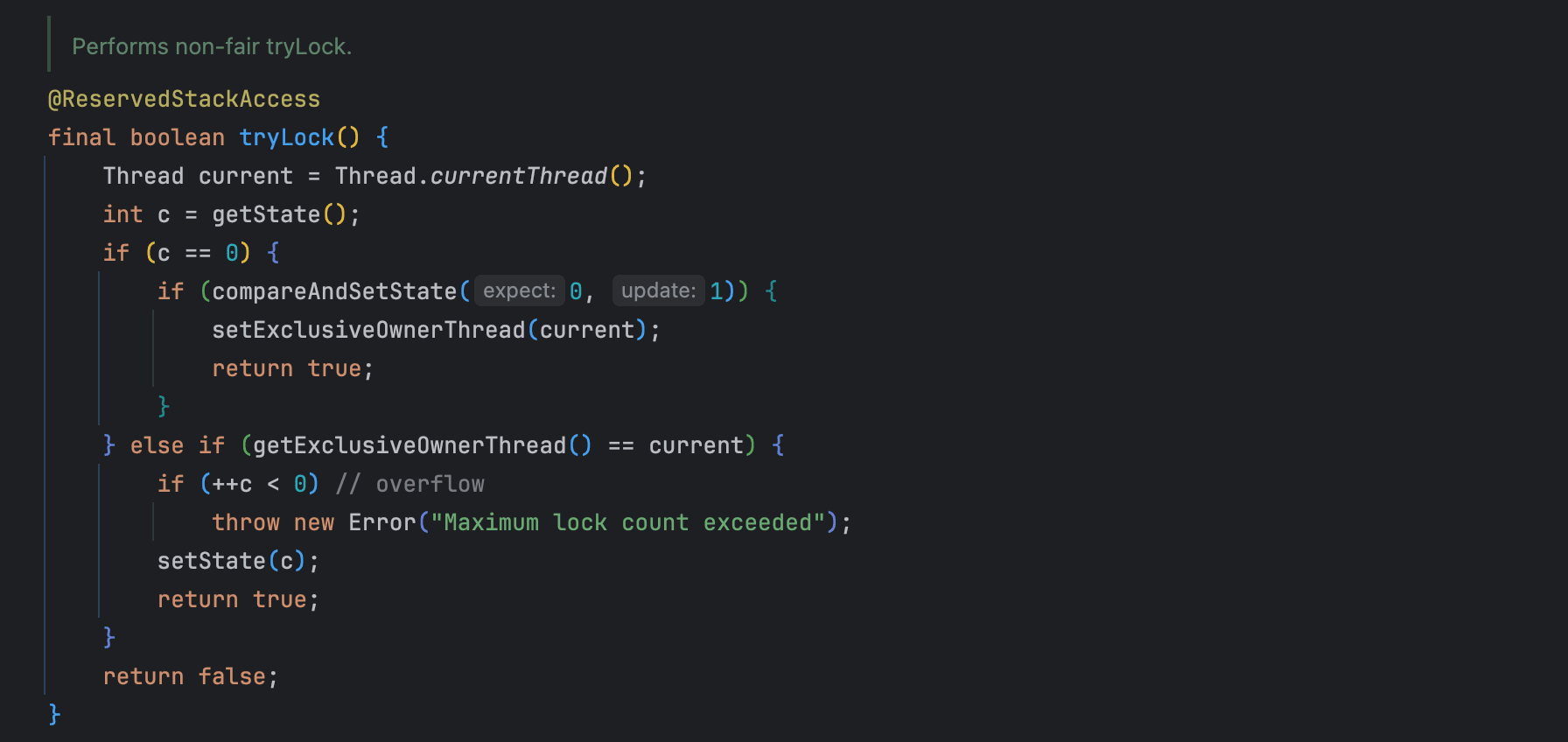
해당 코드로 이슈를 파악할 수 있다.
fun main() {
val lock = ReentrantLock()
for (i in Long.MIN_VALUE..Long.MAX_VALUE) {
lock.lock()
println(lock.holdCount)
}
}
Condition
await, signal 사이 동작은 다음과 같은 특징을 가진다.
await은 락을 획득하고 대기하기 위한 메서드다.signal은await으로 대기하는 스레드를 깨운다.
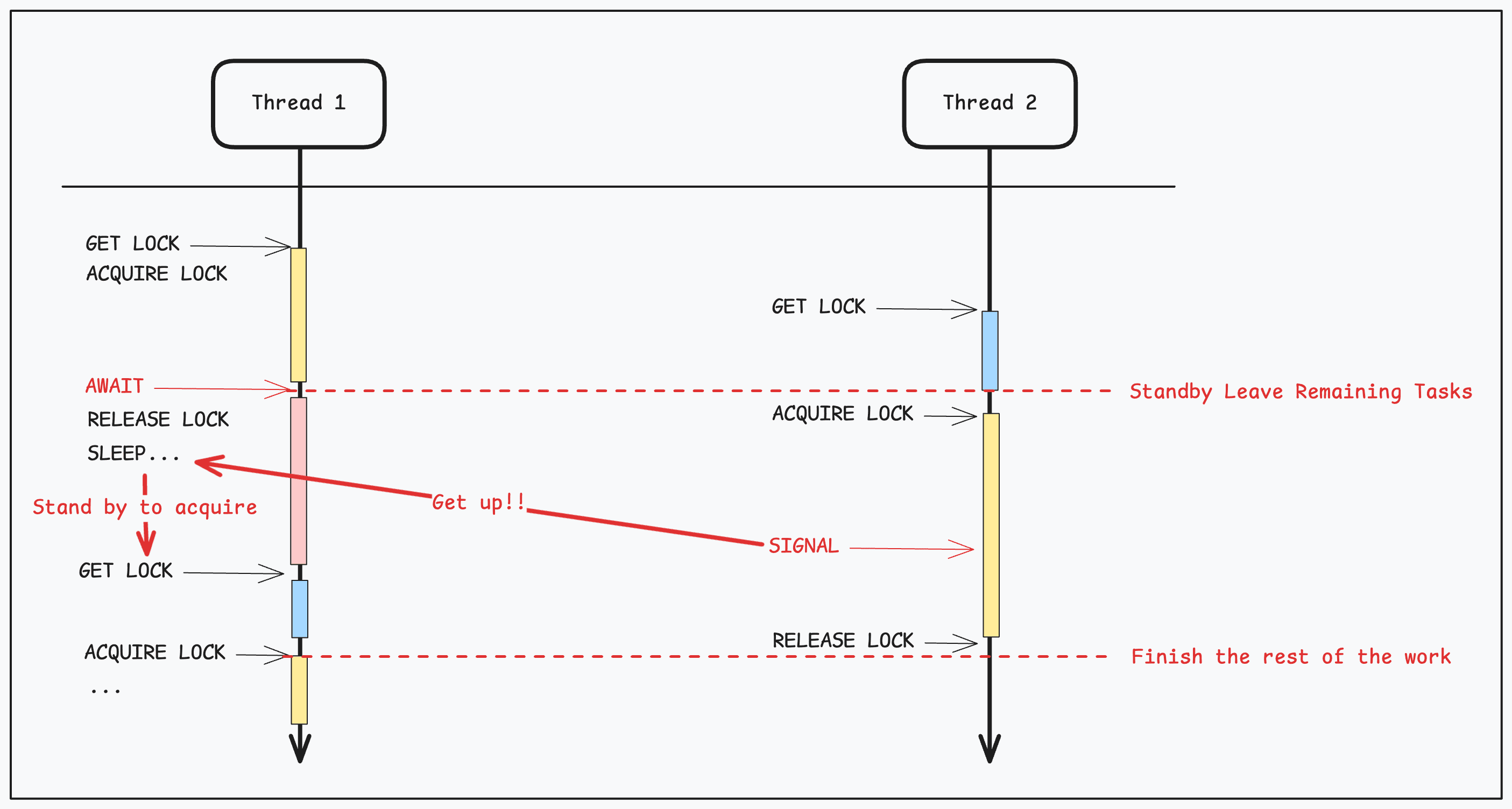
즉, await 하면 가진 lock을 해제하고 대기한다. 이후 signal을 받으면 await이 풀리고 락을 획득하기 위해 대기하게 된다.
다음과 같은 케이스에서 확인 가능하다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
condition.await();
Thread.sleep(100);
System.out.println("hello~");
lock.unlock();
} catch (Exception ignored) {
} });
Thread consumer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
Thread.sleep(300);
condition.signal();
System.out.println("bye~");
lock.unlock();
} catch (Exception ignored) {
} });
producer.start();
consumer.start();
}
Condition은 다음 케이스처럼 특정 조건에 만족하기 위해서 대기하는 경우에 사용 가능하다.
private static class ProducerConsumerExample {
private final int BUFFER_SIZE = 5;
private final Queue<Integer> buffer = new PriorityQueue<>();
private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition notFull = lock.newCondition();
private final Condition notEmpty = lock.newCondition();
public void produce(int item) throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (buffer.size() == BUFFER_SIZE) {
System.out.println("Buffer is full, waiting...");
notFull.await();
}
buffer.offer(item);
System.out.println("Produced: " + item);
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public int consume() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (buffer.isEmpty()) {
System.out.println("Buffer is empty, waiting...");
notEmpty.await();
}
int item = buffer.poll();
System.out.println("Consumed: " + item);
notFull.signal();
return item;
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
대기하는 방식은 두 개로 신호를 받을 때까지 대기하는 방식과 버퍼를 계속해서 확인하는 방식이 있다.
- 신호 받을 때까지 대기한다.
- 버퍼 안을 계속 확인한다.
해당 방식은 뮤텍스와 스핀락과 유사하다. 스핀락은 작업자가 많아질 수록 경쟁 조건이 치열해지는데 이런 경우 뮤텍스 방식으로 경쟁 조건을 완화할 수 있다.
Fairness
ReentrantLock은 공정성 옵션을 추가할 수 있다. 공정성 옵션을 추가하면 먼저 요청한 스레드부터 실행한다. 반면 ReentrantLock에 공정성 옵션을 추가하지 않으면 경쟁하는 스레드 중 무작위로 선택된다.
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true);
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
Thread consumer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
Thread.sleep(5);
lock.lock();
condition.signalAll();
System.out.println("hello~");
lock.unlock();
} catch (Exception ignored) {
}
});
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
final int finalI = i;
Thread producer = new Thread(() -> {
try {
lock.lock();
condition.await();
System.out.println("bye~" + finalI);
lock.unlock();
} catch (Exception ignored) {
}
});
producer.start();
}
consumer.start();
}
공정성 옵션을 가지면 다음과 같은 특징을 가진다.
- 대기 시간 예측 가능하다.
- 공정성 옵션을 선택한 경우보다 성능이 상대적으로 낮다.
비공정성 특징을 가진다면 일부 스레드가 기아 상태가 될 수 있음을 주의하고 상황에 맞게 사용할 필요가 있다.